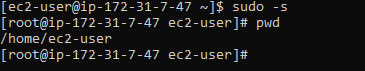
1. pwd
Print the current working directory.
2. ls
List all files and directories in the current directory.
ls -l : Listing all files
ls -a : Lists all files, including hidden files (.) dot file is hidden files.
ls -al or ls -l -a or ls -la : Formatted listing including hidden files.
ls -lh : Shows file sizes in a human-readable format (Size KB, MB, Date & Time, File name, Owner amd Group, Link). Reverse Order Listing.
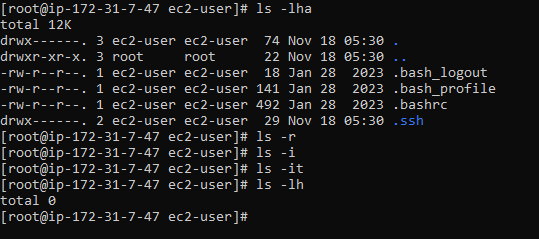
ls -lha : Show hidden files (those starting with a dot).
ls -r : Lists files and directories in reverse alphabetical order. Sorting by Modification Time.
ls - i :Displays the inode number of each file along with the file name. Colorized Listing.
ls -it : Lists files sorted by modification time, newest first. Recursive Listing.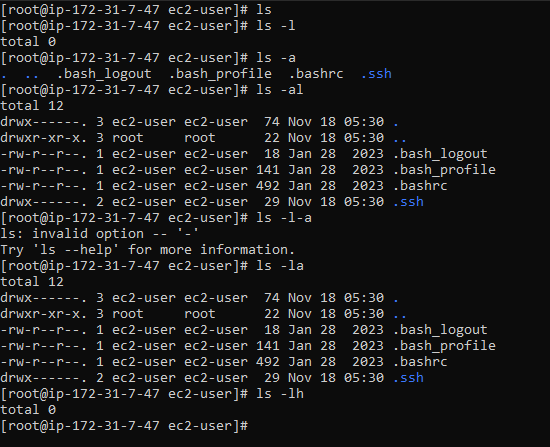
3. cd :
Change the directory
cd / : Go to the root directory.
cd .. : One step back
cd : One folder to another folder
cd ~ : Change to the home directory of the current user
cd - : Go back to the previous directory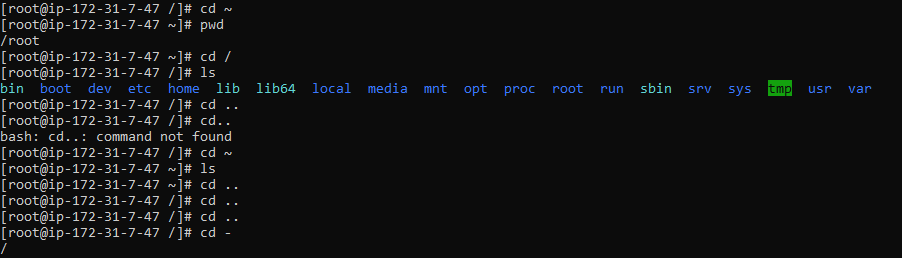
4. mkdir
======> Create a folder (example : prit)
Create a multiple folder
=====> mkdir prit1 prit2 prit3
Create a directory with intermediate directories (create parent directories).
mkdir -p parent_directory/sub_directory/sub_sub_directory
=====> example : folder prit1
=====> mkdir -p local1/local2/local3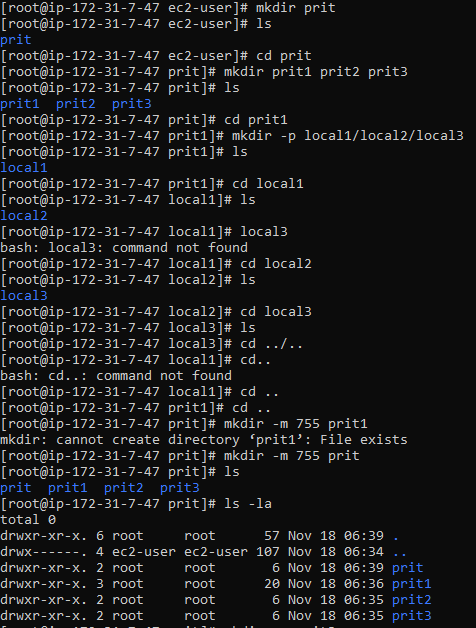
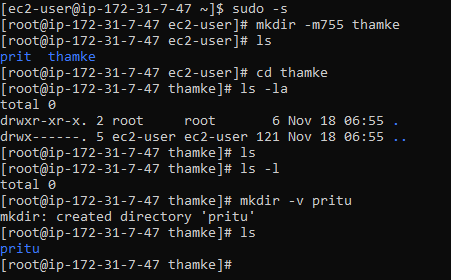
Create a folder with specific permissions set at the time of creation.
=====> mkdir -m 755
Create folder with verbose output to show what is being done.
=====> mkdir -v
5. rmdir
Remove an empty folder
6. rm
Remove files or folder
rm [file name]
rm -r [folder name]
rm -f [folder name]
rm -fr [folder name]
rm -v [folder name]
rm -rvf [file name] ==== full delete
under temp delete : =====> rm -rvf * (data name)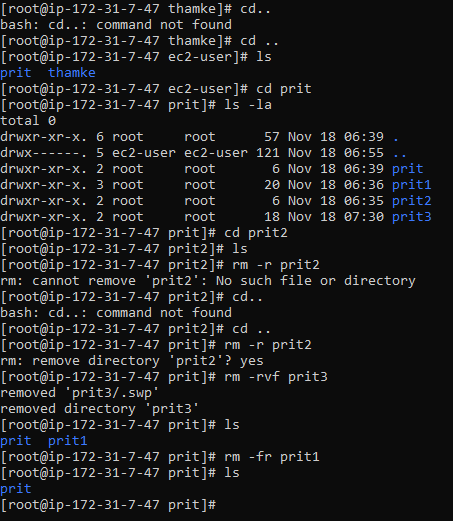
7. echo : Display a line of text/ they are use message print .
8. cat : displays the contents of new.txt
1. Display the content of a single file anu
2. 2. Concatenate multiple files and display the content cat anu,ekta,deepa
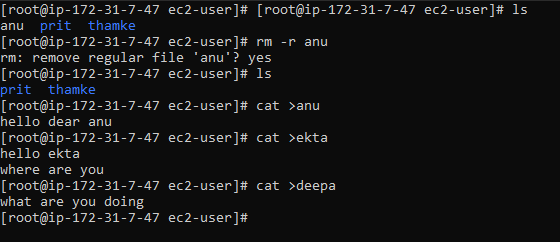
3. Concatenate files and redirect the output to a new file cat anu deepa > mahi
4. Append content of one file to another cat anu >> deepa
5. Display line numbers while viewing the content of a file cat -n anu [modify file = cat >>file name]
ctrl +d === save the file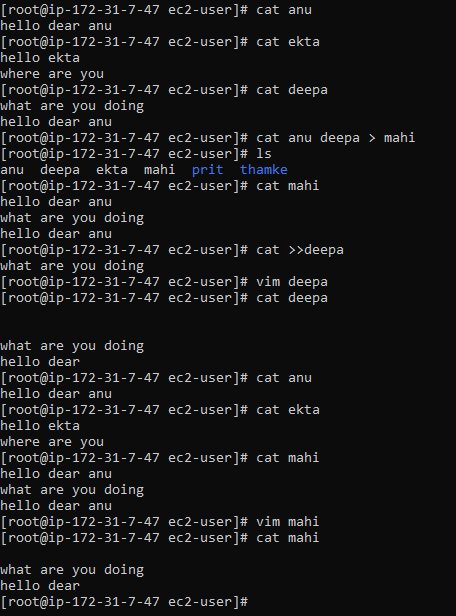
9. more :
View the contents of a file page by page
more anu
View multiple files sequentially
more anu deepa
Display a specific number of lines at a time
more -num 20 filename.txt
Start viewing from a specific line
more +100 filename.txt
View the contents of a file with line numbers
more -n filename.txt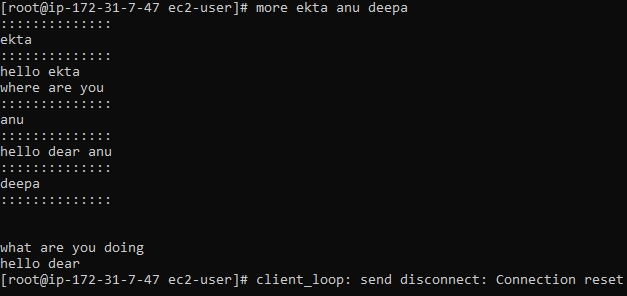
10. head & tail Command
The head command displays the first few lines of a file
Display the first 10 lines.
head prit
Specify the number of lines
head -n 20 prit
Display the first 50
head -c 50 filename.txt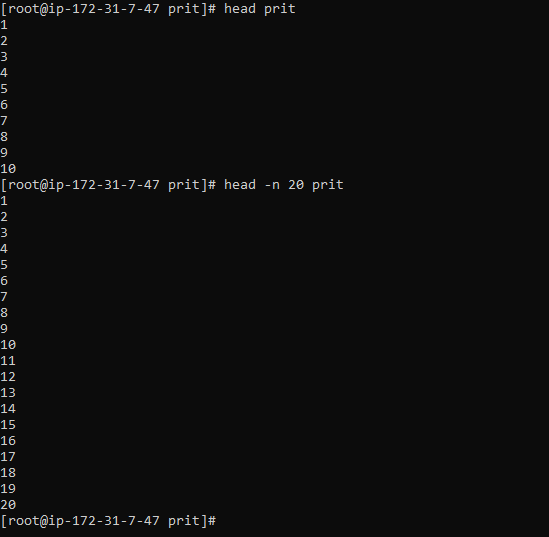
tail :
The tail command displays the last few lines of a file
Display the last 10 lines
head prit
Specify the number of lines
tail -n 20 prit
Display the last 50
tail -c 50 prit
Monitor file changes in real-time
tail -f prit
The -f option is very useful for monitoring log files as they get updated. It will display new lines as they are added.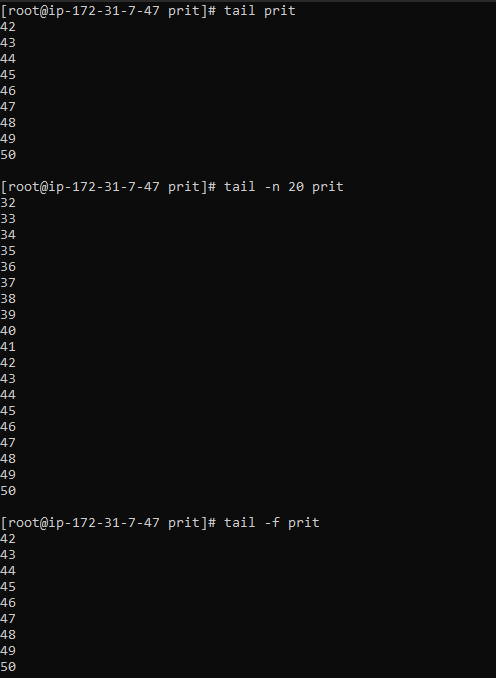
11. tac
its display the file in reserve order (from last line)
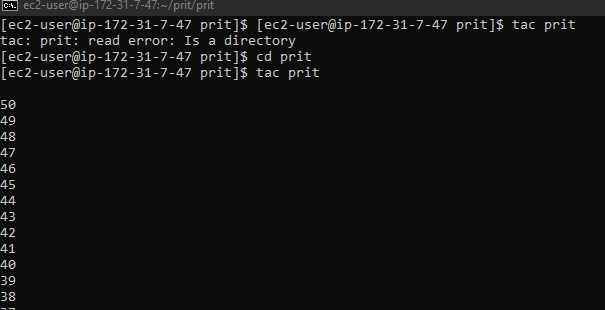
12. id
used to display the user ID & group ID

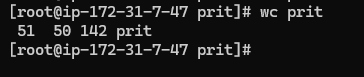
13. wc
used to count the lines, words and characters in a file.
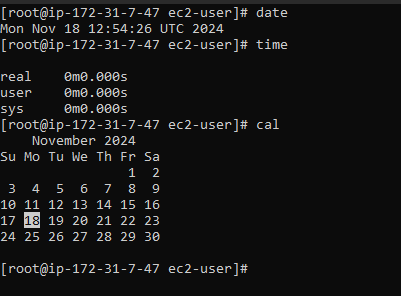
14. date : used to display date, time, timezone and more.
15. time : used to display the time to execute a command.
16. cal : used to display the current months calendar with the current date highlighted.
17. clear : used to clear the terminal screen.
18. exit : used to exit from the current shell.
19. sleep : used to hold the terminal amount of time, it takes time in seconds.
20. mv : used to move a file and directory from one to another location.
mv <file name> <another name>