- free : Display memory usage statistics.
2. uname : print system information
3. df : Report file system disk space usage.
4. du : Estimate file and directory space usage.

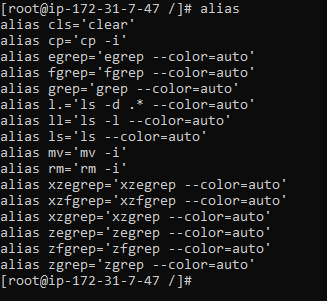
5. alias : it allows users to designate a name to a single command or even a string of commands. So programmers can give a short name before executing it.
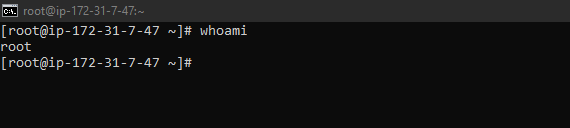
6. whoami : Displays the current user name.
7. nano : Opens a simple text editor in the terminal.
8. vi : Opens a powerful text editor (Vim).
9. man : Displays the manual for a command.
man ls10. uname : Prints system information.
uname -a11. uptime: Shows how long the system has been running.
12. ps: Displays information about running processes.
ps aux
13. top : Displays and updates sorted information about processes.
top14. more : Displays file content one page at a time.
more file.txt15. less : Similar to more, but with backward navigation.
less file.txt16. wc : Counts words, lines, or characters in a file.
wc -l file.txt17. hostname : Displays the system hostname.
hostname18. sort : Sorts lines in a file.
sort file.txt19. uniq : Removes duplicate lines.
sort file.txt | uniq20. whereis : Linux is generally used to see the exact location of any command typed after this.
21. unalias : To remove a defined alias, use the unalias command.
22. exit : To exit the current terminal session.
23. clear : Use the clear command to clear the contents of the terminal quickly
24. passwd : Use the passwd command to alter your password from the terminal.
25. apt and yum : Package managers help install, delete, and manage software packages on Linux systems.
1. For Ubuntu, use the APT package manager:
apt install <package name>2. For CentOS, use yum:
yum install <package name>26. file : The file command provides information about a file, printing the file type and the contents type.
file <filename>27. useradd : The useradd command creates a new user on a Linux system.
sudo useradd <username>28. userdel : Use the userdel (user delete) command to remove a user from the system.
sudo userdel <username>29. chmod : Use the chmod (change mode) command to change file and directory permissions. The command requires setting the permission code and the file or directory to which the permissions apply.
chmod 777 file.txt30. chown : The chown command (change ownership) changes the ownership of a file or directory, To transfer ownership.
for example
sudo chown john:developers example.txt
1. john:developers: Specifies the new owner (john) and the new group (developers).
2. example.txt: The file whose ownership you want to change.