The Internet is a global network of interconnected computers that communicate using standard protocols to share data across the world.

In simple words:
The Internet works by breaking data into small pieces (called packets), sending them through cables and routers, and reassembling them at the destination.
Let’s understand step-by-step.
Step-by-Step: What Happens When You Open a Website?
Suppose you open www.google.com in your browser.
Step 1: You Enter a Website Name (Domain Name)
You type: www.google.com
But computers don’t understand names — they understand IP addresses (like 142.250.183.36).
So your system asks:
👉 “What is the IP address of google.com?”
This is done using:
DNS (Domain Name System)
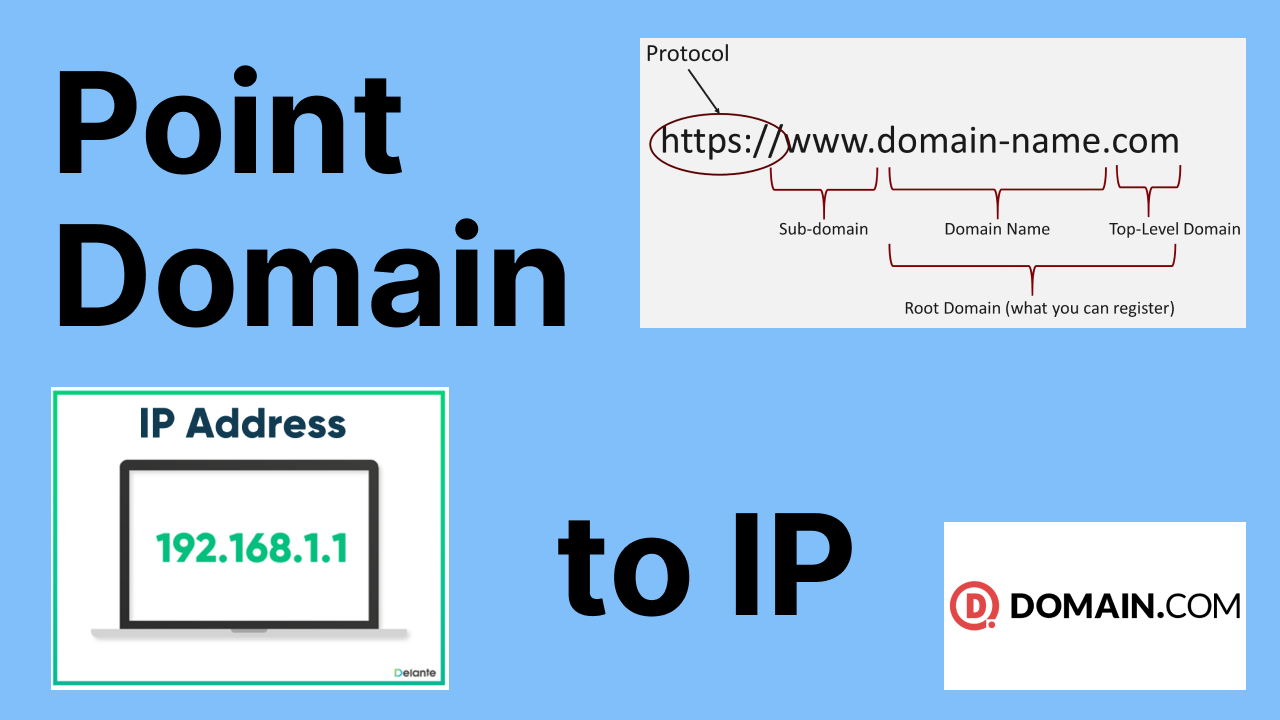

DNS converts:
www.google.com → 142.250.x.x
Step 2: Your Data Is Broken into Packets
Your request is divided into small units called data packets.
Each packet contains:
- Source IP
- Destination IP
- Data
- Sequence number
Think of it like sending a book in many small envelopes.
Step 3: Packets Travel Through Routers
The packets travel through:
- Your WiFi Router
- Your ISP (Internet Service Provider)
- Multiple backbone routers
- Google’s data center
Each router checks:
“Where should I send this packet next?”
And forwards it toward the destination.
Step 4: Server Responds
The website server (Google’s server) receives your request and sends back:
- HTML
- CSS
- JavaScript
- Images
Again in packets.
Step 5: Your Browser Reassembles the Data
Your computer:
- Collects all packets
- Arranges them in correct order
- Displays the webpage
And you see the website
Technologies That Make Internet Work
1️⃣ TCP/IP Protocol
- TCP → Ensures data arrives correctly
- IP → Provides addressing system
2️⃣ Routers
Forward packets between networks.
3️⃣ DNS
Converts domain names to IP addresses.
4️⃣ Cables
- Fiber optic cables
- Undersea cables
- Wireless signals
Real Example Flow (Interview Style)
When a user types a URL:
- DNS resolves domain to IP.
- TCP connection is established (3-way handshake).
- HTTP/HTTPS request is sent.
- Server processes request.
- Response is returned.
- Browser renders content.
Simple Analogy
Internet works like a postal system:
| Internet | Real Life |
|---|---|
| IP Address | Home Address |
| Data Packet | Letter |
| Router | Post Office |
| DNS | Contact Directory |
| TCP | Courier tracking |