HTML (HyperText Markup Language) is the standard language used to create and structure web pages. It allows you to define the layout and organization of content on the web. HTML is made up of a series of elements or tags, such as <h1>, <p>, <div>, and more, that instruct the web browser on how to display the content. These tags are typically written in pairs: an opening tag and a closing tag, with content in between.
<h1>Welcome to My First Website</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph of text.</p>
HTML is essential for building the structure of a webpage, including headings, paragraphs, links, images, and other elements.
Setting Up Your Environment
To start coding HTML, you need:
- A Text Editor: You can use any text editor like Notepad (Windows), TextEdit (Mac), or a code editor like Visual Studio Code, Sublime Text, or Atom.
- A Web Browser: Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, or any browser will be fine to view your HTML files.
Basic Structure of HTML
An HTML document starts with a DOCTYPE declaration and is wrapped in <html> tags. The basic structure looks like this:
<html>
<head>
<title>First WebPage</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello World</h1>
<p>My first paragraph.</p>
</body>
</html> <html>: The root element of the document.
<head>: Contains metadata like the title, character set, and other important info.
<body>: The content of the web page goes here.
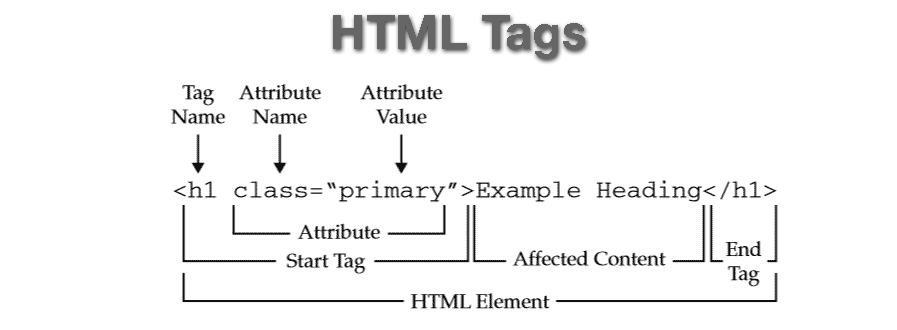
What is an HTML Tag?
An HTML tag is a special keyword enclosed within angle brackets (<>). It defines the structure and elements of a webpage, such as headings, paragraphs, images, and links.
<h1> to <h6>: Headers for different levels of content.
<p>: Paragraph tag.
<a>: Anchor tag for creating links.
<img>: Image tag to embed images.
<ul> and <ol>: Lists (unordered and ordered).
<div> and <span>: Containers for grouping content.
Example of using these tags:
<h1>This is a Heading</h1>
<p>This is a paragraph of text.</p>
<a href="https://www.example.com">Click here to visit Example.com</a>
<img src="image.jpg" alt="An example image">
<ul>
<li>Item 1</li>
<li>Item 2</li>
<li>Item 3</li>
</ul>
Attributes in HTML Tags
HTML elements often use attributes to provide additional information. Attributes are always specified inside the opening tag.
Example of attributes:
<a href="https://www.example.com" target="_blank">Visit Example.com</a>
<img src="image.jpg" alt="A beautiful scenery" width="500">
href: Specifies the link’s destination.
target="_blank": Opens the link in a new tab.
src: Specifies the image source.
alt: Provides alternative text if the image cannot be displayed.
width: Specifies the width of the image.

Working with Forms
Forms are an important part of HTML. They allow users to input data. A basic form looks like this:
<form action="/submit_form" method="POST">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text" id="name" name="name" required>
<br><br>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email" id="email" name="email" required>
<br><br>
<input type="submit" value="Submit">
</form>
<form>: Wraps the form elements.
<label>: Describes a form element.
<input>: Creates an input field for the user to fill in.
<textarea>: Used for multiline text inputs (like comments or descriptions).