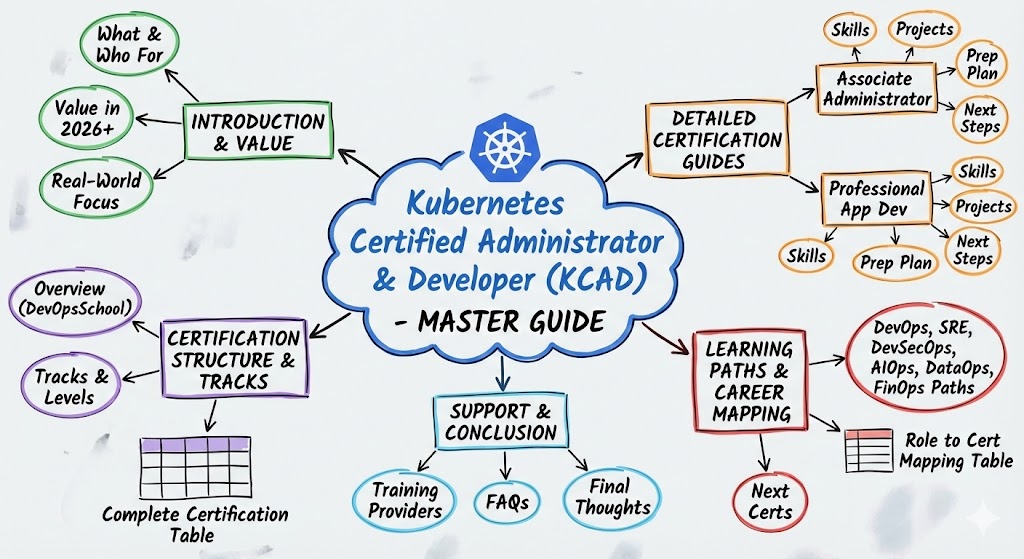
Introduction
Modern software delivery relies on the speed and reliability of container orchestration. Consequently, engineers who pursue the Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) credential gain a significant advantage in the competitive cloud-native market. This guide explores how this comprehensive program from DevOpsschool equips professionals with the skills to manage complex, production-grade clusters. By mastering these principles, you ensure that your applications remain scalable, secure, and resilient against the demands of global traffic.
The Core Mechanics of the KCAD Program
The Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) functions as a performance-based validation of your technical abilities. Instead of asking you to choose from a list of answers, the program places you inside a live terminal where you must solve real-world infrastructure problems. You interact directly with the Kubernetes API to create pods, configure networking, and fix broken nodes. This hands-on approach ensures that anyone who passes the exam can actually perform the duties of a platform engineer in a high-pressure environment.
Who Should Enroll in This Training?
This certification path serves a wide variety of technical roles, from backend developers to full-stack architects. System administrators who want to modernize their skill set find the infrastructure modules particularly rewarding. Similarly, developers learn how to package their code for maximum efficiency within a containerized ecosystem. In the Indian tech sector and global markets, recruiters prioritize candidates with this certification because it proves they possess practical, ready-to-use expertise.
Why This Credential Matters Today
Organizations across the globe are moving away from static servers in favor of dynamic, automated platforms. The Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) remains relevant because it focuses on the open-source standards that power the entire cloud industry. By earning this certificate, you demonstrate that you can manage workloads on any major provider, including AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure. Furthermore, this expertise protects your career against the rapid shifts in specific vendor tools by grounding you in fundamental orchestration logic.
Program Structure and Accessibility
The certification program lives on the Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) and operates under the DevOpsschool umbrella. It divides the learning process into manageable modules that cover everything from basic pod creation to advanced security hardening. The assessment environment mimics a professional workstation, requiring you to use command-line tools like kubectl to manage resources. This setup guarantees that your certification reflects your true ability to handle enterprise-level deployments.
Mapping Your Career Growth
The KCAD path offers a structured journey from basic competency to expert-level mastery. You begin by understanding the core building blocks of a cluster before moving into specialized tracks that align with your specific job goals. This progression allows you to build a portfolio of skills that covers both development and administration. Whether you aim to become a lead developer or a senior SRE, this certification provides the technical foundation you need to move up the corporate ladder.
Comparison of Certification Focus Areas
| Focus Area | Primary Responsibility | Key Kubernetes Objects | Industry Application |
| Administration | Cluster health and setup | Nodes, RBAC, ETCD | Infrastructure Engineering |
| Development | App deployment and scaling | Pods, Deployments, Services | Software Engineering |
| Security | Hardening and compliance | NetworkPolicies, Secrets | DevSecOps |
| Operations | Monitoring and updates | Probes, ConfigMaps, PVs | Site Reliability (SRE) |
Detailed Exploration of KCAD Skill Tracks
Track 1: Cluster Administration and Infrastructure
What it is
This track focuses on the “under-the-hood” components of Kubernetes. It validates your ability to install, configure, and maintain the actual servers that run your containers.
Who should take it
Cloud engineers and system admins who are responsible for the uptime of the entire platform should prioritize this track.
Skills you’ll gain
- Initializing clusters with high-availability configurations.
- Managing persistent storage via CSI drivers.
- Troubleshooting node connectivity and scheduling issues.
- Performing manual cluster upgrades and backups.
Real-world projects you should be able to do
- Deploy a production-ready cluster on virtualized hardware.
- Restore a corrupted cluster using an ETCD snapshot.
- Implement a multi-tenant environment using Namespaces and RBAC.
Preparation plan
- 7–14 days: Study the core control plane components and practice basic Linux administration.
- 30 days: Build multiple clusters from scratch and experiment with different CNI plugins.
- 60 days: Focus on master-node troubleshooting and cluster-wide security audits.
Common mistakes
- Neglecting to practice the installation process on bare-metal or raw VMs.
- Forgetting to verify the status of the Kubelet during node failures.
- Over-relying on cloud-managed services instead of learning the manual configuration steps.
Best next certification after this
- Same-track option: Certified Kubernetes Security Specialist.
- Cross-track option: Terraform Associate.
- Leadership option: Principal Infrastructure Architect.
Track 2: Application Development and Orchestration
What it is
This track centers on how to run applications effectively. It proves you can design resilient systems that handle traffic spikes and hardware failures without downtime.
Who should take it
Software developers and DevOps engineers who focus on the application lifecycle should pursue this specialization.
Skills you’ll gain
- Creating multi-container pod patterns (Sidecars/Adapters).
- Configuring Liveness and Readiness probes for self-healing.
- Managing application state with PersistentVolumes.
- Executing rolling updates and blue-green deployments.
Real-world projects you should be able to do
- Migrate a monolithic web app into a set of microservices.
- Set up an Ingress controller to route external traffic to internal services.
- Scale a deployment automatically based on custom metrics.
Preparation plan
- 7–14 days: Master YAML syntax and the basic
kubectlimperative commands. - 30 days: Practice designing complex deployments with environment variables and secrets.
- 60 days: Conduct mock exams that focus on debugging failing application pods.
Common mistakes
- Using “latest” tags on images instead of specific versioning.
- Leaving sensitive data in plain text within the YAML files.
- Failing to define resource requests and limits for containers.
Best next certification after this
- Same-track option: Cloud-Native Developer Certification.
- Cross-track option: AWS Certified Developer.
- Leadership option: Technical Lead / Staff Engineer.
Specialized Learning Paths for Professionals
DevOps Path
The DevOps path focuses on the bridge between code and production. You learn to automate the delivery pipeline so that every code commit can flow safely into the Kubernetes cluster. This path emphasizes tools that manage the lifecycle of your containers automatically.
DevSecOps Path
This specialization puts security at every stage of the development process. You will learn to scan images for vulnerabilities, enforce network isolation, and manage encryption keys. It ensures that your high-speed deployments remain safe from external threats.
SRE Path
The Site Reliability Engineering path prioritizes system uptime and performance. You will learn to use observability tools to monitor cluster health and set up automated alerts. This path is ideal for those who enjoy solving the “puzzle” of why a system is underperforming.
AIOps / MLOps Path
This track explores the intersection of artificial intelligence and orchestration. You will learn how to schedule GPU-intensive tasks and manage the large datasets required for machine learning models. It prepares you for the future of intelligent, automated infrastructure.
DataOps Path
DataOps focuses on the challenges of stateful applications like databases. You will learn to manage data persistence so that your information remains intact even if a container restarts or moves to a different node.
FinOps Path
The FinOps path teaches you how to keep cloud costs under control. You will learn to analyze resource usage and implement quotas that prevent your Kubernetes clusters from overspending your company’s budget.
Role-Based Certification Mapping
| Professional Role | Recommended Certification Track |
| DevOps Engineer | Admin + Developer Tracks |
| SRE | Admin Track + Observability Tools |
| Platform Architect | Admin Track + Advanced Networking |
| Full-Stack Developer | Developer Track + Cloud Basics |
| Security Engineer | Security Specialist + Admin Core |
| Data Engineer | Developer Track + StatefulSet Mastery |
| IT Manager | Foundational Overview + FinOps |
Advancing Beyond the KCAD
Deep Specialization
After completing your KCAD, you should consider the Security Specialist (CKS) exam. This allows you to master the most critical and highest-paying aspect of Kubernetes: protecting the cluster from sophisticated cyberattacks.
Horizontal Skill Expansion
Broadening your knowledge to include infrastructure-as-code tools like Terraform or Ansible complements your Kubernetes skills. This makes you a complete engineer who can build the cloud, the cluster, and the application.
Moving into Technical Leadership
Combining your hands-on KCAD skills with management training prepares you for leadership roles. You will be able to speak the language of both business and engineering, making you an ideal candidate for CTO or VP of Engineering positions.
Leading Support Providers for KCAD Training
DevOpsSchool
DevOpsSchool provides a robust learning environment that balances deep theory with practical labs. Their mentors guide you through the most difficult parts of the KCAD curriculum, ensuring you understand the “why” behind every command. They focus on making you job-ready by simulating the exact challenges you will face in a corporate setting.
Cotocus
Cotocus offers specialized training that helps organizations migrate their legacy systems to the cloud. Their courses emphasize architectural best practices and long-term maintainability. Professionals who choose this provider gain a high-level perspective on how Kubernetes fits into a global business strategy.
Scmgalaxy
Scmgalaxy operates as a massive community resource for DevOps professionals. They offer a variety of tutorials and peer-to-step support systems that help you stay updated on the latest Kubernetes features. It is a great place to network with other engineers and share real-world troubleshooting tips.
BestDevOps
BestDevOps focuses on high-intensity training programs that get you certified quickly. They use streamlined teaching methods to cover the most important exam objectives in a short period. This is the perfect choice for busy engineers who need to level up their skills without taking a long break from work.
devsecopsschool.com
This provider focuses exclusively on the security layer of the cloud-native stack. They teach you how to build “security-first” cultures and implement automated defense mechanisms within your clusters. Their courses are essential for anyone handling sensitive data.
sreschool.com
Sreschool.com specializes in the reliability aspect of Kubernetes. They teach you how to maintain five-nines of uptime through advanced monitoring and automated incident response. Their training is designed for those who want to work at the highest levels of site reliability.
aiopsschool.com
Aiopsschool.com prepares you for the next generation of infrastructure by teaching you how to run AI workloads on Kubernetes. They focus on the unique resource requirements of machine learning and how to automate the AI lifecycle.
dataopsschool.com
This school addresses the complexities of data management in a containerized world. They teach you how to build robust data pipelines and ensure that your databases stay performant and available within a cluster environment.
finopsschool.com
Finopsschool.com provides the financial knowledge that modern engineers often lack. They teach you how to read cloud bills and optimize your Kubernetes resources to save money while maintaining peak performance.
Frequently Asked Questions (General)
- How does the KCAD exam work?The exam takes place in a browser-based terminal environment where you must complete a set of tasks on live Kubernetes clusters within a two-hour limit.
- Is there any theory in the exam?No, the exam is 100% practical. You will not find any multiple-choice or true/false questions.
- What is the passing score?You typically need a score of 66% or higher to pass the exam and receive your certificate.
- Can I use Google during the test?No, you are restricted to using only the official Kubernetes documentation website as a reference.
- How long is the certification valid?The certification is valid for two years, after which you must renew it by passing the latest version of the exam.
- Do I need a powerful computer to take the test?No, the exam runs in a web browser, so you only need a stable internet connection and a computer that supports the proctoring software.
- How many retakes do I get?Most exam registrations include one free retake if you fail on your first attempt.
- Is the KCAD recognized by major companies?Yes, it is one of the most widely recognized and respected certifications in the tech industry today.
- What is the difference between CKA and KCAD?CKA focuses on cluster administration and setup, while KCAD (as represented in this guide) covers the full spectrum of both management and development.
- Do I need to know a programming language?While you don’t need to write code in the exam, understanding the basics of application architecture and YAML is essential.
- How long does it take to get results?You will usually receive your results via email within 24 to 48 hours after the exam ends.
- Can I take the exam in India?Yes, you can take the exam online from any location in India that has a private room and a reliable internet connection.
Specific FAQs on the KCAD Program
- Which version of Kubernetes is used in the exam?The exam environment usually matches the version of Kubernetes that was stable roughly three months before the exam date.
- What terminal shell does the exam use?The exam environment provides a standard Bash shell with common utilities and the
kubectltool pre-installed. - Are there any restrictions on my workspace?Yes, you must have a clean desk and be alone in a quiet, well-lit room. The proctor will check your environment via your webcam.
- Can I use an external monitor?Most proctoring rules require you to use only one monitor. You should check the latest rules on the official exam site before starting.
- Is the use of aliases allowed?Yes, many candidates set up aliases like
alias k=kubectlat the start of the exam to save time. - What happens if my internet drops during the exam?The proctoring system usually allows you to reconnect, but your exam timer will continue to run.
- How many questions are in the exam?The exam typically consists of 15 to 20 different tasks of varying difficulty and point value.
- Is there a lab environment provided during the training?Yes, training providers like DevOpsSchool include dedicated lab environments that mimic the actual exam interface.
Final Thoughts: Is the KCAD Path Right for You?
Pursuing the Kubernetes Certified Administrator & Developer (KCAD) represents a significant commitment to your professional growth. This certification does more than just validate your knowledge; it proves that you can solve difficult problems in real-time. As the industry continues to embrace cloud-native technologies, the demand for certified experts will only grow. If you want to move beyond basic container usage and become a true master of orchestration, this is the path you need to follow. Stay consistent with your labs, master the command line, and you will find that the career rewards far outweigh the effort required.